第一作者简介: 王露(1988—),女,硕士研究生,主要从事水文地质环境地质研究。Email:xiaolu1990_2008@163.com。
通信作者简介: 李铎(1963—),男,博士,教授,主要从事水文地质环境地质研究。Email:Liduo556688@126.com。
温度的变化能够改变水体的环境,引起周围环境中的离子吸附解吸作用的变化。不同于其他土壤,砂土的保水保肥能力更差,砂土地区一旦发生氨氮(NH4+-N)污染,情况会更加严重和突出。为防治砂土地区N H4+-N污染提供理论依据与技术支持,通过N H4+-N的静态吸附试验,研究不同温度条件下N H4+N在粗砂、中砂、细砂中的吸附转化特征,得到如下结论: 在试验设置的温度区间内,总的趋势是温度越低,砂土对N H4+-N的吸附量越高,表明温度升高对N H4+-N的吸附有抑制作用,这主要是因为吸附过程中会产生弱放热效应,进而降低渗滤介质对N H4+N的平衡吸附量; 在25~30 ℃区间内存在硝化与反硝化作用的临界温度,当温度低于临界温度时,N H4+-N吸附量的减少主要是由于发生了硝化反应,当温度高于临界温度时,N H4+-N的吸附量减少主要是由于发生了反硝化反应。
Temperature variation can change water environment, which causes the variation of adsorption and desorption of the ions in surroundings. The capability of preserve moisture and fertility in sand is worse than that in the other soil. Once the pollution of ammonium nitrogen (N H4+-N) happens in sand, the problems will be more serious. To provide theory and technology for preventing the pollution of ammonium nitrogen (N H4+-N) in sand, the authors studied the adsorption and transformation characteristics of ammonium nitrogen (N H4+-N) in coarse sand, medium sand and fine sand under different temperature conditions, based on the static adsorption experiment. The results show that in the setup temperature range, the lower the temperature is, the higher the adsorption capacity of ammonium nitrogen (N H4+-N) is, which indicates that the adsorption of ammonium nitrogen (N H4+-N) is inhibited by high temperature. And it is the cause that low exotherm of adsorption process can reduce the capability of equilibrium adsorption for ammonium nitrogen (N H4+-N). The transform temperature of nitrification and denitrification is between 25℃ and 30℃. When the temperature is lower than the transform temperature, the reduction of adsorption capability for ammonium nitrogen (N H4+-N) is due to nitrification. And when the temperature is higher than the transform temperature, the reduction of adsorption capability for ammonium nitrogen (N H4+-N) is due to denitrification.
温度的变化能够引起分子间的热运动, 从而改变水中溶解氧的含量, 引起周边环境的变化, 进而引起周围环境中的离子吸附解吸作用的变化[1, 2, 3]; 温度的变化还会影响微生物的生物活性, 进而改变水体的环境[4, 5]。关于氨氮(N
实验所用的砂样取自河北省石家庄市滹沱河河漫滩和一级阶地。砂样取回后经晾干、研磨、筛分后用于物理性质分析, 其分析结果如表1所示。
| 表1 砂样的基本物理性质 Tab.1 Basic physical properties of the sand samples |
方法一: 配制N
方法二: 为了更确切地了解实验温度对砂土对N
氨氮(N
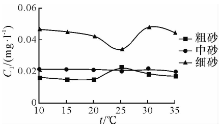 | 图2 溶液NO2--N浓度随温度变化曲线Fig.2 Concentration-temperature curves of NO2--N in the upper liquids of experimental samples |
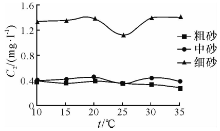 | 图3 溶液NO3--N 浓度随温度的变化曲线Fig.3 Concentration-temperature curves of NO3--N in the upper liquids of experimental samples |
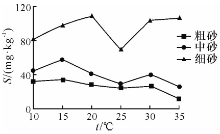
由图1— 图3可知: 随着温度的升高, 粗砂对N H4+-N 的吸附量在10~15 ℃区间逐渐升高, 15~25 ℃区间逐渐下降, 25 ~30 ℃区间略微上升, 30~35 ℃区间又明显下降; N
中砂对N H4+-N 的吸附量在10~15 ℃区间逐渐升高, 15~25 ℃区间逐渐下降, 25~30 ℃区间略微上升, 30~35 ℃区间又略微下降; N
细砂对N H4+-N 的吸附量在10~20 ℃区间逐渐升高, 15~25 ℃区间逐渐下降, 25~35 ℃区间逐渐上升; N
综上所述, 砂土对N H4+-N的吸附量总的趋势是随着温度的升高, 吸附量减少。
影响介质在不同温度下对N
(1) N
(2)扩散传质。随着温度的升高, 溶液黏度降低, 水分子和N
氨氮(N
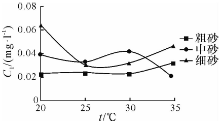 | 图5 溶液NO2--N浓度随温度的变化曲线Fig.5 Concentration-temperature curves of NO2--N in the upper liquids of experimental samples |
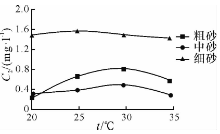 | 图6 溶液NO3--N随温度的变化曲线Fig.6 Concentration-temperature curves of NO3--N in the upper liquids of experimental samples |
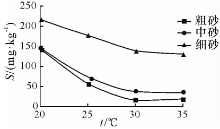
由图4— 图6可知: 随着温度的升高, 粗砂对N
随着温度的升高, 中砂对N
随着温度的升高, 细砂对N
(1)随着温度的升高, 含水介质对N
(2)在25 ~30 ℃区间存在硝化作用与反硝化作用的临界温度, 当温度小于临界温度时, N
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
| [1] |
|
| [2] |
|
| [3] |
|
| [4] |
|
| [5] |
|
| [6] |
|
| [7] |
|
| [8] |
|
| [9] |
|
| [10] |
|
| [11] |
|
| [12] |
|