第一作者简介: 马嘉宝(1997—),男,硕士研究生,主要从事环境科学、健康地质调查研究等方面工作。Email: shy3312567@126.com。
持久性有机污染物(pervistent organic pollatants, POPs)环境地球化学调查是分析掌握POPs化学性质、迁移转化、环境归趋的重要手段。基于文献对近年来POPs的环境地球化学调查研究进展进行了综述,总结出以下3个方面的结论: ①POPs普遍具有环境难降解、长距离迁移性、生物蓄积性和高生物毒性等特征,POPs浓度数据在世界各地不同环境中介质中被广泛报道,随着历史累积和持续释放,POPs已经成为危害生态系统、人类健康的重要风险,已有调查监测数据显示,当前我国部分水、土检测样品POPs浓度水平较高; ②POPs可在大气-水体-沉积物或者大气-土壤等不同环境界面中相互迁移,进而污染地下水并迁徙到地表系统的每个角落,这种迁移转化与POPs成分及环境介质的物理化学性质、温度、pH值等因素密切相关; ③当前,我国相关机构对大气、水体、土壤和底泥等环境介质中的部分POPs类型缺少连续系统的调查监测,难以对POPs污染状况、长周期变化规律进行系统分析研究。建议今后应当加强大气-土壤-水界面长周期动态监测工作,进一步完善POPs的监测、分析方法标准方法,并开展系统的环境地球化学综合分析研究,为实施环境污染防治和生态修复提供理论和实践支撑。
The environmental geochemical survey of persistent organic pollutants (POPs) is an important mean to study and master its chemical properties, migration, transformation and environmental fate. Three inclusions were summarized based on the research progress of environmental geochemical investigation and research of POPs in recent years. ① POPs generally have characteristic of environmental refractory, long-distance migration, bioaccumulation and high biological toxicity, and the concentration data of POPs have been widely reported in different environmental media around the world. The POPs have become an important risk that endangers ecosystems and human health, with the historical accumulation and continuous release. According to the existing survey and monitoring data, the concentration levels of POPs from test samples of partial water bodies and soil are currently high in China. ② POPs can migrate among different environmental interfaces such as atmosphere-water-sediment or atmosphere-soil, then it can contaminate ground water and migrate to every corner of the surface system. This migration and transformation are closely related to the composition of POPs and the physical and chemical properties, temperature, pH and other factors of the environmental medium. ③ there is a short of continuous and systematic investigation and monitoring about some types of POPs in environmental media such as the atmosphere, water bodies, sediment, and soil, the relevant institutions in China, which results in difficult systematic analysis and research on the pollution levels and long-term changes of POPs. It is suggested that the long-term dynamic monitoring of the atmosphere soil water interface should be strengthened and the monitoring and analysis methods, standards and methods of POPs should be improved. The systematic environmental geochemical comprehensive analysis and research also should be carried out to provide theoretical and practical support for the implementation of environmental pollution prevention and ecological restoration.
近年来, 经济快速增长、能源消耗、工业化和城市化带来持久性有机污染物(persistent organic pollutants, POPs)的广泛生产和利用, 给环境、生态系统和人类健康带来严重影响[1]。目前, 全球已有120多个国家签署了《斯德哥摩尔公约》, 共有29种POPs列入禁用化学物质名录。受污染管控、生态修复的理论和实践需求, 近年来POPs环境地球化学调查研究日益受到重视, 逐渐成为地质科学、环境科学、生态学等众多学科交叉的研究热点, 其研究方向与进展主要体现在以下4个方面。①POPs环境地球化学特性研究。POPs的环境行为、生物富集、暴露水平与健康风险持续受到关注, POPs的环境持久性、远距离迁移性、生物累积性等特征逐渐得到广泛证实, 有力推动了POPs相关化学品的全球监管。②POPs污染状况的调查监测。随着《GB/T 14848— 2017地下水质量标准》[2]、《GB 3838— 2002地表水环境质量标准》[3]、《GB 15618— 2018土壤环境质量农用地土壤污染风险管控标准》[4]、《DZ/T 0288— 2015区域地下水污染调查评价规范》[5]等多个标准规范的颁布实施, 三氯苯、四氯苯、苯并芘等POPs污染物被先后纳入调查监测范围, 短链氯化石蜡、全氟辛烷磺酸等新型POPs的调查监测也逐渐得到重视, 针对POPs排放集中区、南北极和青藏高原环境敏感区、重要生态功能区中多种环境介质(水、空气、土壤、沉积物、食物、生物样品等)中的大量POPs浓度数据被广泛报道。③POPs 的地球化学迁移转化研究。在POPs调查监测基础上, 研究总结了不同种类POPs在水、土、气中的分布规律以及不同界面之间的迁移转化规律。④气候变化背景下POPs在区域或全球范围内的迁移循环研究蓬勃发展。该领域2004年前鲜有报告, 近10 a 来取得重要进展。特别是针对南北极、青藏高原等地区的洋流、季风、冰川等研究表明, 气候变化在直接或者间接地影响着POPs的排放、传输、储存、分布、降解和最终归宿。本文重点围绕POPs的污染情况、环境地球化学行为、迁移转化规律等进行综述, 以期为后续的POPs调查监测、生态修复工作提供基础资料。
POPs化学结构复杂, 同类物和异构体有数千种, 其中许多都是特定系列或家族的成员, 其源头主要来自杀虫剂使用、工业排放、垃圾焚烧、生活排放等途径[6]。主要包括: 有机氯农药(organochlorine pesticide, OCPs), 如六六六(hexachlorocyclohexane, HCHs)、滴滴涕(dichlorodiphenyltrichloroethane, DDTs)等; 多环芳烃(polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons, PAHs), 包含萘、蒽、菲、芘等150余种化合物; 多氯联苯(polychlorinated biphenyls, PCBs), 根据氯原子取代数和取代位置不同, 共有209种同系物; 多溴联苯醚(polybrominated diphenyl ethers, PBDEs), 包括5、8、10溴联苯醚等同系物亦超过200种; 全氟化合物(per-and polyfluoroalkyl substances, PFASs), 包含全氟辛烷磺酸(perfluorooctane sulphonate, PFOS)、全氟辛烷羧酸(perfluorooctanoic acid, PFOA)等; 此外, 还包括氯化石蜡、二恶英、氯酚等有机化合物。虽然POPs结构复杂、种类繁多, 但具有非常鲜明的环境地球化学特征。
POPs在化学组成上富含氯、溴、氟等卤族元素, 化学键能大, 热稳定性强, 在自然环境中具有很强的抗生物降解、抗光解、抗水解和抗化学分解作用。POPs在大气中半衰期约为数天, 但在水体、土壤、水下沉积物中半衰期可达数十年以上[7]。对照2008年欧洲化学品管理署《化学品注册、评估、授权与限制》法规(附件7)[8]规定的半衰期标准(表1), 大多数POPs可纳入持久性和高持久性范围。根据赋存环境介质不同, POPs半衰期也有差异, 如PAHs在水中半衰期为7~60 d, 在水下沉积物中半衰期为8个月至6年。异狄氏剂(C12H8C16O)在土壤中的半衰期为4~8 a, 七氯(C10H5C17)在土壤中的半衰期为 0.11~5.5 a[6, 7]。PFOA在有氧无氧状况下均有极强的抗生物降解、抗水解和抗光解的特性, 在水中光化学的半衰期达到256 a[9]。由于POPs降解缓慢, 即使所有新来源立即被消除, 它们仍将在自然环境中存在很长时间。
大多数POPs具有较强挥发性, 在环境温度下POPs能够从土壤、水体和植被挥发到空气中, 以气相或者与大气中悬浮颗粒物、气溶胶结合, 通过全球蒸馏效应和蚱蜢效应, 在温度较低或适宜的环境介质表面发生吸附和沉降, 其挥发、冷凝、沉降的顺序可以经常重复, 使其在全球湖泊、海洋、大气及其气溶胶、土壤、水体沉积物、冰雪、地下、地表水以及生物体中广泛分布, 并以此为迁移介质在局部、区域甚至全球范围内长距离迁移转化[10, 11], 污染偏远地区的生态环境。例如, 自20世纪70年代以来, 虽然HCHs、DDTs、PCBs等化学品已经被禁止或严格管制, 但近年来南北极地区POPs大量“ 气、水、土、生” 监测研究证实[12, 13, 14, 15, 16, 17, 18, 19, 20, 21, 22, 23], 在从未使用过POPs或者远离人类活动的地区的各类环境介质中依然不同程度检出POPs(表2)。
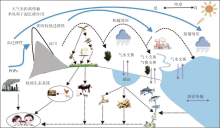
典型POPs中, 只有α 、β 、γ -HCH异构体、PFOS、PFOA等少数污染物具有较高水溶性[24]。绝大多数POPs具有疏水和亲油脂的特性, 在自然生态系统中, 其倾向于分配并吸附或储存在生物脂肪、有机质沉积物及其他有机质颗粒物中[7, 24]。抗降解作用、新陈代谢和亲脂性的综合作用, 驱动POPs不断在食物链中集聚, 其浓度会随着食物链的延长而逐级升高, 使得位于食物链顶端的高级生物体内的POPs浓度比周围环境介质的浓度提高多个数量级[25]。通常是某几种或某几族POPs相互作用, 最终对生态系统和身体健康造成极大危害(图1)。
近年来国内外学者对生物体内POPs浓度水平及生理毒性进行了大量监测和试验研究, 研究发现POPs在世界各地不同等级、不同种类、不同生存环境中的动植物体内器官、脂肪、血液中普遍分布, 并与环境浓度明显正相关。中国湖泊生物体内Σ HCHs含量为0.50~3 405.67 ng/g, 16种优先控制的PAHs总含量为289.00~17 877.26 ng/g[26]。范夏瑞等[27]通过提取过去30 a发表文献中的数据, 估算了我国POPs在食物中的暴露水平: DDTs (1.4~27.1ng/g)、HCHs(1.8~29.3 ng/g)、PBDEs (0.046~2.82 ng/g)、PCBs(0.05~7.57 ng/g)、PFOA(0.02~0.97 ng/g)、PFOS(0.000 82~2.76 ng/g)。数据分析表明, DDTs、HCHs、PBDEs、PCBs等大部分传统 POPs 的环境暴露水平呈现下降趋势, 然而其它类型 POPs下降并不明显, 存在较高程度的健康风险[27]。全球六大洲母乳样品中也都检测出POPs(图2)[28], 俄罗斯远东母乳样本中POPs浓度水平(HCHs+DDTs+PCBs)范围为23~878 ng/g(平均151.4 ng/g)[29]。越来越多证据表明, POPs不仅具有致癌、致畸、致突变性, 而且具有内分泌干扰作用, 对生殖系统、免疫系统、神经系统等产生毒性, 损伤皮肤和内脏器官。
POPs主要通过工农业直接排放、地表径流、雨水冲刷、大气干湿沉降等途径释放到水体, 并在空气— 水体— 水下沉积物间发生迁移转化, 具有复杂的环境地球化学过程。
我国对POPs监测始于20世纪80年代, 前期以OCPs为主, 后期逐步拓展到PCBs、PAHs、PFASs等新型污染物。调查发现, 部分水体的POPs污染浓度水平值得高度关注(表3)。
| 表3 国内部分水体POPs浓度水平[30, 31, 32, 33, 34, 35, 36, 37, 38, 39, 40, 41] Tab.3 POPs concentration level in some domestic water bodies[30, 31, 32, 33, 34, 35, 36, 37, 38, 39, 40, 41] |
OCPs作为《斯德哥尔摩公约》首批禁用的12种(其中8种为OCPs)持久性有机污染物, 目前以HCHs、DDTs的检出率最高。从已发表的文献数据上看, 欧美国家流域水体中OCPs浓度一般在几至几百ng/L[42]。我国流域水体HCHs和DDTs的质量浓度分别⫹5 000 ng/L、1 000 ng/L。统计发现, 中国境内17个省市区49个湖泊水体Σ HCH4(α 、β 、γ 、δ -HCH)浓度范围为0.25~195 ng/L, DDTs及其降解物(dichloro-diphengl-dichloroethane, DDD)、(dichloro-diphengl-dichloroe thylene, DDE)的平均浓度分别为(12.8± 23.5) ng/L(n=30)和(12.8± 24.6) ng/L(n=24)[43]。受近年来我国禁用及限制使用OCPs和自然降解影响, 其浓度范围呈逐渐下降趋势, 如1995年白洋淀水体中Σ OCPs浓度检出量为3 050 ng/L, 2008年检出量为13.21 ng/L, 2016年检出量在2.62~6.13 ng/L之间[33, 44]。但非洲、印度等发展中国家部分流域水体污染水平依然较高, 如非洲尼日尔河Σ OCPs样本浓度水平为(1 138.0± 246.7) ng/L[45], 可能与这些发展中国家禁用或限制OCPs类农药时间较晚有关。
PAHs的脂溶分配系数大, 易于与有机质结合, 水下有机质沉积物为其主要汇区, 但各类水体中PAHs依然不同程度检出, 浓度一般在ug/L级以下。《地表水环境质量标准(GB 3838— 2002)》[3]将PAHs中的苯并芘纳入特定检测项目, 但未明确PAHs总指标。截止2019年2月公开数据, 中国26个湖泊水体Σ PAH16平均浓度水平为(360.0± 433.8) ng/L(n=26)[43]。个别水体PAHs检出浓度处于中高水平, 如辽河流域水体中Σ PAHs浓度水平为 94.78~2 931.62 ng/L[36]。长江武汉段水源地Σ PAHs浓度水平为57. 04~475.79 ng/L, 其中苯并芘浓度水平为1.49~15.28 ng/L[37], 高于《地表水环境质量标准(GB 3838— 2002)》[3]规定的2.8 ng/L限值。
PCBs在水体中一般以低氯取代的单体溶解态为主, 而高氯取代的 PCBs更易分配到水下沉积物中。根据已报道文献数据, 国内水体Σ PCBs的检出范围在Nd(检出限)~1 355.30 ng/L[46], 大部分水体浓度监测值在几至几十ng/L之间, 其中26个湖库水体浓度范围为(0.19± 0.12)~(23.1± 22.2)ng/L[43]。对照《地表水环境质量标准(GB 3838— 2002)》[3]中PCBs的限制值(20 ng/L), 部分水体PCBs检测样品浓度存在超标现象, 如长江武汉段饮用水水源PCBs浓度水平为Nd~77.49 ng/L[37]。
PFASs目前已经成为一种新型、最难降解的全球性有机污染物之一, PFAS中以PFOS和PFOA的检出率最高, 一般地表水可达到ng/L水平。这两类化合物兼具亲水基团和疏水结构, 既易溶于水又容易在生物体内累积富集[24]。自2004年以来, 我国一直是PFASs的最大生产、排放国。相比较而言, 国外地表水 PFOA浓度普遍较低, 而我国不同地区地表水PFOA 污染程度差异明显, 部分地区污染水平较高, 如辽河、太湖、钱塘江杭州段及渤海湾等部分水体 PFOS、PFOA浓度水平均大于100 ng/L[47], 上海市地表水Σ PFASs最大含量为362.37 ng/L[48], 辽河PFASs污染浓度可达781 ng/L[49], 远高于我国其他水域, 可能与我国东部氟化工业发展水平高有关。
水体中绝大多数POPs的溶解态浓度非常低, 主要受正辛醇-水分配系数(lgKow)控制。lgKow的数值一般随着POPs 苯环数量、分子量增加而增大, lgKow的数值越大, POPs的疏水性和亲脂性越强, 在水中溶解浓度就越小[30]。吸附态POPs主要吸附于悬浮有机质颗粒物(含小型藻类、浮游动物活体及残体)中, 吸附态POPs比溶解态的POPs随水介质的迁移性更强, 且更不容易被生物降解或者光解, 更容易造成POPs的富集与污染。特别指出的是, 水体中粒径小于0.45 μ m且溶于水的溶解性有机质(dissolved organic matter, DOM), 可通过配位、螯合等作用与POPs结合, 并显著增加POPs水溶性, 提升POPs伴随环境介质的迁移能力[50, 51, 52]。水下沉积物是POPs环境迁移转化的主要归宿, 水中吸附态POPs会随着颗粒物沉降, 最终分配到底部有机质沉积物中并被不同程度检出(表4), 特别是高环数PAHs、高溴代的PBDEs等更容易在水下沉积物中累积, 导致沉积物中的 POPs 浓度通常要比上覆水体中的浓度高几个, 甚至十几个数量级[63]。
| 表4 国内部分水体水下沉积物的浓度水平[32, 36, 37, 53, 54, 55, 56, 57, 58, 59, 60, 61, 62] Tab.4 POPs concentration level of underwater sediments in some domestic water bodies[32, 36, 37, 53, 54, 55, 56, 57, 58, 59, 60, 61, 62] |
调查发现, 我国水域水下沉积物POPs部分样本检测浓度较高, 如珠江三角洲和南海北部海域水下表层沉积物样品的PBDEs含量为12.7~7 361 ng/g, 已经成为目前世界上已报道沉积物中含量较高的区域之一[64]。POPs在水下沉积物中的累积与沉积物化学成分及其结构形态、温度、pH值等因素密切相关。一般来讲, 沉积颗粒物的粒径越小, 其有机质含量越高, 吸附 POPs 的能力越强, 而POPs的浓度就大, 在水体中的解吸能力就越弱, 也就越不利于POPs的迁移和转化[65, 66]。
POPs可以在大气-水体-沉积物不同界面之间迁移, 水体中POPs以蒸发方式进入大气, 大气中POPs也可通过干湿沉降作用再次释放到水体[67], 其平衡过程与大气、POPs化学组分及物理环境相关。水体生物可通过生物吸收、吸附和捕食等途径, 形成生物富集效应, 并显著降低水中溶解态POPs浓度[68]。生物体对POPs的富集效应与其营养级、脂肪含量、年龄和食物链长度呈正相关, 但并非完全一致[25, 51, 65]。当水体发生富营养化时, 浮游生物的生长率和生物量会大大增加, 而浮游生物的生物富集效应可消耗水中POPs, 导致其在水体中溶解态浓度降低[65], 当超过一定浓度标准时, 就会打破 POPs在水-气界面的平衡状态, 促进POPs 从大气向水体转移[69]。反之, 当大气中POPs浓度降低时, 水体向大气再挥发出POPs的可能性也会大大增加[70]。随着POPs排放的减少, 水-气交换方向可转为挥发或者平衡。如20世纪80年代以来, 随着OCPs在全球范围内长期禁用或者严格使用, OCPs的海(水)— 气交换方向已经发生倒转, 由大气干湿沉降为主逐渐转变为水体向大气的二次释放[71]。
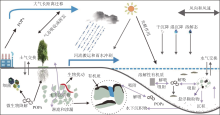
水-沉积物界面是POPs地球化学循环的重要区域(图3)。水下沉积物则既是POPs的归宿, 也是水体POPs污染的重要内源。温度升高时, 水下沉积物中的 POPs 的释放作用明显增强, 使得水体中溶解态POPs浓度升高。POPs还可通过沉积物的再悬浮进入水体中, 造成水体中吸附态POPs浓度呈量级增加, 形成水体的POPs“ 二次污染” [24], 因而对水体沉积物中的POPs监测更为关键。例如, 当湖泊在秋季分层结束时, 沉积物中的 POPs 会随着颗粒物的再悬浮再次进入水体中, 颗粒再悬浮作用可造成水体中 POPs 沉降通量会比大气沉降通量高 1~2 个数量级[72]。风浪、潮汐、灌溉、拖网等作用导致水动力作用增强, 或者在底栖生物扰动的情况下, 也可以显著改变沉积物-水界面的POPs吸附和解吸过程, 从而导致水下沉积物中的POPs向水体迁移。研究显示, 大型底栖动物促使挪威奥斯陆陆港沉积物中的PAHs、PCBs和DDTs等污染物分别以每天243 pmol/m2、19.6 pmol/m2和13.6 pmol/m2的速度向水体释放[73]。通过交换模型研究安徽太湖水体和沉积物中发现, HCHs 迁移方向是由沉积物到水体, 历史沉积物释放已成为太湖水体中HCHs主要来源[74]。同时, 水溶性较高的PFOS、PFOA、低氯代PCBs以及与DOM呈吸附或结合态的POPs, 更容易通过渗流区、土壤间隙水渗透向深层迁移, 成为深层土壤和地下水的潜在污染源[24, 52, 75]。
土壤是一个由固-液-气组成, 介质松弛, 物理化学性质相对稳定的复杂系统, 是POPs在陆地生态环境系统重要的富集场所, 通过经历一系列吸附、解吸和迁移转化过程, 可能引发生态污染风险。
世界各国土壤中均不同程度存在POPs。土壤中的POPs可通过喷洒农药、施用化肥、工业废气与废水排放、大气干湿沉降、雨水冲刷、地表径流等途径进入土壤[76]。POPs在土壤中的浓度, 一般与当地工业化和城市化程度密切相关, 人类活动和时间累积同样发挥着重要作用。DDTs和 HCHs是土壤中最普遍的OCPs有机污染物, 欧美、东亚等地球随着OCPs禁用和降解时间的延长, 总体上未达到污染水平或属于低污染水平[77], 而非洲少数地区农地土壤污染风险较高, 如加纳中部某农场OCPs浓度为2 100~15 500 ng/g[78]。
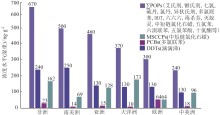
我国PCBs在土壤中的空间分布或残留浓度与PCBs产品的使用密切相关, 其中高氯代 PCBs 通常呈现典型点位污染且在点位土壤中含量明显高于低氯代同系物[79]。近年来, PAHs在全国范围内土壤污染越来越普遍, 并呈现出从城市工业带到农村土壤扩散的态势。统计2000— 2020年公开发表166篇文献发现, 我国表层土壤PAHs含量中位值为675.70 ng/g, 其含量峰值出现在表层或亚表层(0~40 cm), 部分城区或工业区附近污染较为严重[80]。如我国西安市区居民区土壤中 PAHs平均值高达50.06 μ g/g, 是PAHs致癌浓度的两倍[81]。PBDEs是世界产量最大的溴系阻燃剂, 土壤中沉积物中绝大多数为BDE-209、BDE-153、BDE-183等化合物单体[82], 一般在土壤中的分布浓度随离工业区距离增加而减小, 大多数污染地区土壤中以高溴代的PBDEs为主, 偏远地区土壤中则以挥发性较强的低溴代PBDEs为主[83]。土壤中全氟化合物以PFOA、PFOS 检出率最高, 其他新型POPs污染物也不断被检出[84]。
土壤对POPs固存作用主要通过有机质分配, 土壤间孔隙水溶解, 矿物颗粒的表面点位吸附等方式实现, 与土壤粒度、有机碳含量、温度、pH值等因素紧密相关, 不同种类或者相同种类但分子量不同的POPs的吸附作用也存在明显差异[75]。通常土壤粒度越小, 有机质含量越高, 土壤对POPs的吸附作用越强, 使得POPs的抵淋虑、抗降解能力也就越强, 越不易解吸和迁移[85, 86]。当土壤颗粒物的粒径一致时, 土壤中POPs浓度与土壤有机质含量总体呈正相关[87]。pH值影响土壤矿物颗粒表面电荷、POPs的沉淀溶解、微生物活性, 一般说来, PH值越低, 土壤对POPs的吸附能力越强[88]。土壤中氧气和光照有限, POPs有氧微生物降解特别是光解作用较弱, 厌氧还原脱卤是土壤中POPs降解的最重要形式[89], 但迄今为止尚未发现能够有效降解PFASs的微生物[90]。实际情况下, POPs需要依赖多个微生物的协同代谢才能完成。
土壤是POPs的“ 源” 与“ 汇” 。土壤中POPs通过挥发作用进入大气, 大气中POPs也可通过干湿沉降作用进入土壤, 并沿土层纵向迁移[91], 进而污染深部土壤及地下水(图3)。以PAHs为例, 通常浅层土壤高环数POPs占比高, 随深度增加POPs含量及高环数占比逐步降低[92]。
陆地植物也在POPs循环中扮演重要角色, 在有机碳含量高的陆生林草系统, 极易将大气中亲脂性POPs吸附截留, 而植被凋落物又会将植被体内和表面吸附的 POPs 迁移至森林土壤, 在土壤物化性质、土壤表层覆盖物、微生物活动、雨水淋虑等因素影响下, 使得POPs固存在土壤中或向深部迁移[93]。
在土— 气交换方面, 通常POPs中的低氯代PCBs、低溴代PBDEs、低环数PAHs更容易挥发进入大气[94, 95]。传统理论认为, 挥发性强的HCHs等POPs倾向于通过降雨降雪沉降至地表, 挥发性差的十溴二苯醚(BDE-209)等主要吸附存在大气悬浮颗粒物上并进行长距离大气迁移。最新研究证实, 即使挥发性极低的POPs也可通过气态迁移, 并成为污染物累积的重要来源[83]。在POPs全球迁移方面, 受全球分馏和冷凝作用的影响, POPs存在由低纬度向高纬度定向迁移富集的趋势, POPs也可以沿海拔高度发生分馏冷凝, 使得地球南北极、青藏高原成为POPs的重要“ 汇区[96, 97, 98]” 。有研究发现, 我国夏季东南季风可将东南区POPs污染物输送到东北汇区[99]。青藏高原南部和北部的 POPs则分别来自南亚和欧洲的输入[100], 高原南部大气中DDTs的含量明显高于北部, 印度季风及其降水是 DDTs 输入青藏高原的动力。
温度被认为是影响POPs大气浓度、沉降-挥发过程以及二次污染排放的首要因素。一般来讲, 温度上升会提升土壤中POPs的挥发性。“ 全球蒸馏效应” 模型证实, 气温每升高1 ℃, POPs挥发性就会增加10%~15%[101]。气候变化可能会加强持久性有机污染物从水、土壤和冰川中的再排放过程。长期监测发现, 虽然全球POPs排放逐渐减少, 但北美洲五大湖地区六氯苯和HCHs的大气浓度依然持续升高, 根本原因是温度升高驱动了两种污染物从土壤、水体中的二次挥发释放[102]。北极地区监测发现, OCPs、PCBs等污染物也表现出冬季最小值和夏季最大值的季节性变化, 重要原因是夏季温度升高加速海冰消融会使得已沉积POPs污染物重新释放进入大气[71]。
POPs可发生局部、区域和全球尺度的迁移、转化和循环, 具有复杂的环境地球化学过程, 其科学调查研究难度与深度以及污染的严重性、复杂性和长期性远远超过常规污染物。中国作为经济快速增长的发展中国家和化学品生产消耗大国, POPs所引起的环境污染和健康风险比其他国家更为复杂。同时针对部分污染物的监测能力还十分有限, 缺乏明确的标准监测手段。推进生态文明建设, 必须深化POPs调查监测和环境地球化学研究, 为评估环境与健康风险, 实施环境污染防治和生态修复, 推动健康中国建设提供支撑服务。
(1)统筹开展POPs监测工作。结合实际需要, 在土壤地球化学调查、环境地质调查、水资源调查(地下水监测)、健康地质调查等工作中有针对性地开展相关POPs调查监测工作, 将更多POPs及同系物纳入调查监测范围, 同时加强大气-土壤-水界面一体化联合监测, 开展长周期动态监测工作。
(2)建立和完善统一规范的POPs标准化监测、分析方法。加强POPs在不同环境介质中的主被动采样技术研究发, 满足长期监测、数据分析和变化趋势研究需要。
(3)深化POPs环境地球化学综合研究。加强POPs在不同环境界面迁移转化行为、区域污染迁移过程、POPs与重金属复合效应以及重要工业区和农业区POPs生态污染修复工作。
(4)加强生态、自然资源、农业农村等机构相关POPs调查监测数据共享和集成整合, 形成调查研究合力。
(责任编辑: 刘丹, 王晗)
| [1] |
|
| [2] |
|
| [3] |
|
| [4] |
|
| [5] |
|
| [6] |
|
| [7] |
|
| [8] |
|
| [9] |
|
| [10] |
|
| [11] |
|
| [12] |
|
| [13] |
|
| [14] |
|
| [15] |
|
| [16] |
|
| [17] |
|
| [18] |
|
| [19] |
|
| [20] |
|
| [21] |
|
| [22] |
|
| [23] |
|
| [24] |
|
| [25] |
|
| [26] |
|
| [27] |
|
| [28] |
|
| [29] |
|
| [30] |
|
| [31] |
|
| [32] |
|
| [33] |
|
| [34] |
|
| [35] |
|
| [36] |
|
| [37] |
|
| [38] |
|
| [39] |
|
| [40] |
|
| [41] |
|
| [42] |
|
| [43] |
|
| [44] |
|
| [45] |
|
| [46] |
|
| [47] |
|
| [48] |
|
| [49] |
|
| [50] |
|
| [51] |
|
| [52] |
|
| [53] |
|
| [54] |
|
| [55] |
|
| [56] |
|
| [57] |
|
| [58] |
|
| [59] |
|
| [60] |
|
| [61] |
|
| [62] |
|
| [63] |
|
| [64] |
|
| [65] |
|
| [66] |
|
| [67] |
|
| [68] |
|
| [69] |
|
| [70] |
|
| [71] |
|
| [72] |
|
| [73] |
|
| [74] |
|
| [75] |
|
| [76] |
|
| [77] |
|
| [78] |
|
| [79] |
|
| [80] |
|
| [81] |
|
| [82] |
|
| [83] |
|
| [84] |
|
| [85] |
|
| [86] |
|
| [87] |
|
| [88] |
|
| [89] |
|
| [90] |
|
| [91] |
|
| [92] |
|
| [93] |
|
| [94] |
|
| [95] |
|
| [96] |
|
| [97] |
|
| [98] |
|
| [99] |
|
| [100] |
|
| [101] |
|
| [102] |
|